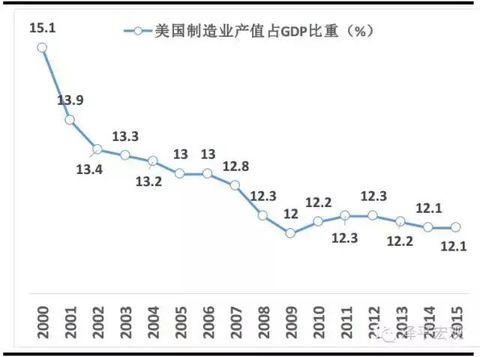
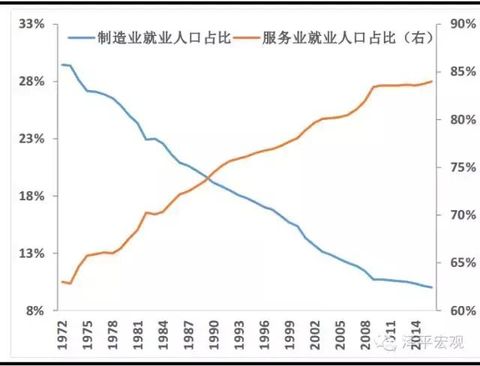
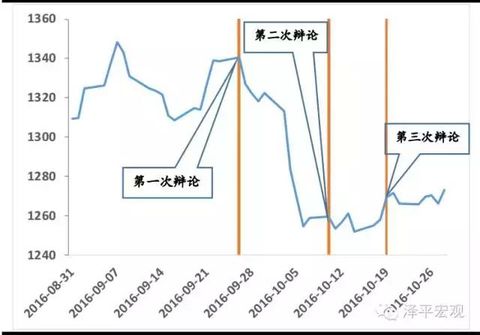
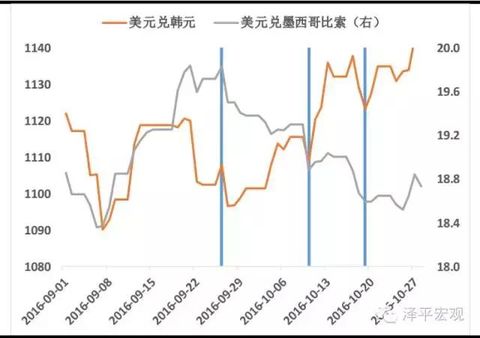
Invite friends to send Hao Li! 185 yuan red envelope waiting for you to take! Fund Mall 1 fold purchase Author: Ren Zeping, Lu Liang Liang Source: Macro Zeping Introduction: The US presidential election entered a period of intense heat. After three rounds of debate, the national voter vote was held in November. Because Hillary and Teplang have broad policy differences in monetary policy, fiscal policy, trade, immigration, and China, the two candidates have distinct personalities and opinions, so whoever enters the White House will have a future economy and market. A completely different impact. Summary: Hilary and Trump's background of growth: a woman who is obsessed with politics vs. wants to be the president's "mouth gun" tycoon. From "first lady", senator, secretary of state to presidential candidate, Hillary is passionate about politics and experienced. If elected, she will become the first female president in American history. Trump was born into a real estate family. He was a successful businessman and entertainment star, winning a black horse in the Republican nomination. The economic policy agenda of Hillary and Trump campaigns essentially reflects the difference between the political and economic ideas of the Democratic Party and the Republican Party and the interests of the interest groups behind it. The Democratic Party is a believer in the Keynesian school. It believes in big governmentism and advocates expanding government power and advocating expansionary fiscal and financial policies. The Republican Party is more like a fan of the Chicago School, advocating a "small government" and pursuing a traditional economic theory that is laissez-faire. Therefore, the ruling ideas of the two-party presidential candidates will be different. The interest groups represented, Hillary represents labor and trade unions, Teplang represents employers and business owners, and Wall Street supports Hillary. Fiscal policy differences: Hillary advocated tax increases, and Tepran advocated spending cuts. Both the Democratic Party and the Republican Party tend to reduce deficits and stimulate the economy, but there are differences in the means of reducing the deficit. Hillary hopes to increase the fiscal source by increasing taxes on the rich. Trump advocates reducing government spending, such as abolishing Obama. Medicare programs and the hiring of new employees in government departments. Another core of Trump’s fiscal policy is tax cuts to stimulate domestic investment and consumption. Both candidates mentioned increasing infrastructure investment to stimulate the economy, and the focus on public service spending is different. Hillary tends to invest in education and medical care, while Trump is more willing to raise defense spending. Differences in monetary policy: Hillary may continue to loosen, and Tepland criticizes low interest rate policy. If necessary, Hillary will use monetary policy to assist her fiscal stimulus, preferring to loose rather than tightening the currency. Trump has repeatedly criticized the distortions caused by the Fed's low interest rate policy. Although the low interest rate environment can reduce the financing cost of infrastructure investment, Trump's remarks may indicate that the low interest rate policy may be adjusted in the future. Trade policy differences: Hillary is conservative but moderate, and Tepran is more radical and anti-global. Hillary’s trade policy began to be conservative, opposed to the TPP, and stopped any trade agreement that hindered job growth and income growth. Trump's trade policy is more radical. To protect traditional industries, he has always advocated trade protectionism and opposed free trade agreements such as NAFTA and TPP. Trump proposed to declare China a currency manipulator and impose a 45% tariff on all Chinese imports. Financial regulatory differences: Hillary advocates strengthening supervision, and Trump advocates deregulation. The market generally believes that Hillary Clinton as a Democratic candidate will continue Obama's regulatory policy, continue the Dodd-Frank Act, rectify Wall Street and dismantle big banks. Trump believes that supervision should be relaxed and it is recommended to abolish the Dodd-Frank Act. Analysis of immigration policy and employment issues: Hillary supports immigrants, and Teplang wants to build walls to stop immigrants. Hillary hopes to continue the Obama administration’s immigration policy and support illegal immigrant families who are chasing the American dream. Trump’s immigration policy is extreme. He claims to be building a wall on the Mexican border and expelling 11 million illegal immigrants. Attitudes and positions toward China: Hillary Clinton is again playing against China, and Trump maintains a tough attitude. In her primary campaign speech, Hillary Clinton once called China "the biggest abuser of global trade" and said that she "will promote the establishment of a fair arena for global trade once elected." In addition to trade issues, Hillary supported the toughness of China on the South China Sea issue. At the same time, Hillary believes that the United States cannot do without China's support and cooperation on issues such as the Korean Peninsula and climate change. Trump’s policy stance on the Chinese issue is tough. Trump does not know much about China, but often criticizes China and blames the US's predicament on China's rise. He once said that after the election, it will strengthen the US military deployment in the East China Sea and the South China Sea and deter China. If Hillary or Trump is elected president of the United States: the impact on the market. 1) Hillary’s policy ideas are more about the continuation and revision of the current Obama administration’s thinking. Trump, on the other hand, represents a policy of “changing the stringsâ€. Because his policy ideas are more radical, he has raised concerns about the uncertainty of the market, but it also reflects the demands of the people for change. 2) Hillary's coming to power indicates that the Fed's monetary policy tightening will be lower than expected, and the stability of the initial policy is also beneficial to the capital market and the US stock market. The risk of uncertainty falls, and the price of gold is negative. The relative openness of Hillary’s foreign trade will drive the recovery of currency exchange rates in emerging market countries, especially those with a very high degree of trade dependence (such as Mexico). The US economy is slowly recovering and the US dollar index is slowly strengthening. 3) Trump's tax cuts are conducive to the recovery of private consumption and the recovery of private investment. Tax incentives in the infrastructure sector will also accelerate investment, and Trump's program will theoretically be more conducive to the rapid recovery of the US economy. Although the low interest rate environment can reduce the financing cost of infrastructure investment, Trump’s remarks may indicate that the low interest rate policy may be adjusted in the future and the US debt will be negative. The toughness of Trump’s foreign policy (including trade and diplomacy) has caused the market to worry about the stability of the future economy, and gold prices may rise in the early days of its administration. The isolationist trade policy will impact the foreign exchange markets and stock markets of emerging economies. table of Contents: 1. The background of Clinton and Trump's growth: a woman who is obsessed with politics VS. I want to be the president's "mouth gun" tycoon 2. Hillary and Trump’s policy differences 2.1 Interest groups represented: Hillary represents labor and trade unions, Teplang represents employers and business owners, and Wall Street supports Hillary 2.2 Fiscal Policy Differences: Hillary advocates tax increases, and Tepran advocates spending cuts 2.3 Monetary Policy Disagreement: Hillary may continue to be loose, Teplang criticizes low interest rate policy 2.4 Trade policy differences: Hillary is conservative but moderate, and Tepran is more radical and anti-global 2.5 Financial regulatory differences: Hillary advocates strengthening supervision, Trump advocates deregulation 2.6 Disagreement between immigration policy and employment: Hillary supports immigration, Teplang wants to build walls to stop immigration 2.7 Attitudes and Positions towards China: Hillary Clinton pulls back and pulls against China, Trump maintains a tough attitude 2.8 Disagreement on ideology, race, and other issues such as the world political landscape 3. Possible development direction of trade policy with China 3.1 History of US Trade Policy with China 3.2 The future direction of Sino-US trade 3.3 Impact of trade protectionism against China on employment in the United States 4. If Hillary or Trump is elected president of the United States: Governing ideas and influence on the market 4.1 If Hillary is elected president of the United States 4.2 If Trump is elected president of the United States 4.3 Impact of different candidates on the market text: The US presidential election is entering a white-hot stage. After three rounds of debate, the national voter vote is held in November. Because Hillary and Teplang have different policy ideas and differences on monetary policy, fiscal policy, trade, immigration, and China, the two candidates have distinct personalities and opinions. Therefore, whoever enters the White House will probably complete the future economy and market. Different effects. 1 Hilary and Trump's background of growth: a woman who is obsessed with politics vs. wants to be the president's "mouth gun" tycoon Hilary, a woman who is obsessed with politics. Hilary Rodham Clinton was born in Chicago in 1947, father Hugh Rodham is a curtain merchant and owner, a conservative Republican; mother Dorothy Rodham is a free housewife. Under the influence of the father who was keen on politics, Hillary became obsessed with politics from an early age and debated various political issues from time to time. At school, Hillary did not hide her enthusiasm for politics, from the picket captain to the student council president. The inconsistency in parental values ​​also has an impact on Hillary’s political beliefs. Hillary Clinton in the middle school era was an out-and-out Republican supporter. The university gradually turned into a determined Democrat and became a passionate candidate for Democratic presidential candidates McGovern and Carter. In 1969, Hillary entered the Yale Law School and studied in the field of children. She became a lawyer after graduating in 1973. She joined the Legal Advisory Panel of the House Judiciary Committee in 1974 and was responsible for investigating the possibility of impeaching President Nixon for the Watergate scandal. Sex. In 1975, Hillary married her Yale classmate Bill Clinton. In 1978, Hillary became the "first lady" of Arkansas. She began her political talent and successfully promoted the reform of the education system in the state. In 1993, Hillary became the "first lady" of the United States, known as the most powerful first lady in history. She actively intervened in the White House decision-making and actively promoted medical reform, but eventually failed because she did not adapt to the political climate of Washington. Two years later, Hillary Clinton stepped out of Clinton’s political aura and was elected to the Senate. She became the first person in American history to be successfully elected as a Senator during the First Lady’s term. After the 9/11 attacks, Hillary Clinton, a senator, supported the war on terrorism and urged the Lord to pass a large number of motions to provide compensation and subsidies to the survivors of the victims. In her “traditional field†of health care, education, and helping the poor children and children, Hillary also promoted a number of legislation. In 2006, Hillary successfully re-elected as a senator. On January 20, 2007, Hillary officially announced that she will participate in the 2008 presidential election, hoping to create the first history of the first female president of the United States. Although she lost to the party’s opponent, Obama, she was invited to serve as the secretary of the new government, without prejudice to its power. Chasing. Hillary’s high pursuit of power prompted her to actively participate in the decision-making process and diplomatic activities of foreign policy during her tenure as Secretary of State. According to statistics, Hillary has visited a total of 112 countries during her four-year tenure, with a total flight time of 2,084 hours, a total journey of 1.53 million kilometers, and a total of 38.42 laps around the earth. State Department officials praised her as the most hardworking Secretary of State in the United States. In February 2013, Hillary stepped down as Secretary of State. On April 12, 2015, Hillary officially announced her candidacy for the 2016 US presidential election and began to chase the presidential throne. On June 7, 2016, Hillary won the Democratic presidential nomination battle and became the first woman in the history of the US election to be nominated by the main political party. If she wins successfully in the national elections in November, Hillary will also become the first female president in American history. Want to be the president's real estate tycoon, entertainment star Trump. Donald John Trump was born in New York City in 1946. The Trump family has been in business for three generations. His father, Fred Trump, is a well-known real estate developer with a good reputation in New York. His mother, Mary Anne. Rump is a Scottish immigrant. Trump followed his father from a young age, and he was conscious of his business. He specializes in economics and real estate research at the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania. After graduating from college in 1968, Trump entered the real estate company founded by his father. In 1975, Trump began to personally supervise the reconstruction of the "Hyatt Hotel", becoming an important milestone in Trump's real estate business. In 1999, Trump renamed the company Trump Group, a group of high-end properties all over the world. Trump not only created a business legend, but also entered the entertainment industry. In 2003, Trump became the producer and host of the ABC reality show "Fei Huang Teng Da". Since the launch of the show, the ratings have soared, and Trump’s popularity has increased, making it a name on the Hollywood Walk of Fame. Trump has repeatedly announced that he is competing for the presidency. In 2012, Trump won the Republican nomination for the US presidential election, but he announced his withdrawal from the US presidential nomination for the Republican nomination. On June 17, 2015, Trump re-elected the US president in New York. Thanks to the high support rate among the Republican Blue-collar voters, Trump has defeated traditional Republican elites such as Scott Walker, Jeb Bush, Marco Rubio and Ben Carson and Carly. Fiorina and other non-traditional candidates won the Republican nomination. On July 21, 2016, Trump officially accepted the nomination of the US Republican presidential candidate. Trump is not a "hardcore Republican". He has changed party membership many times. Before 1987 and 2001-2009, he was a Democrat; he was a Republican from 1987-1999 and 2009. Some people criticized him as "the time of the Democratic Party is more than the Republican Party." It is "the spies of the Democratic Party." Trump's character is a maverick, and he is known for his unremarkable. Because he has no public office experience, he lacks foresight on many policy issues. He has no cover and bold criticism, but he has no creative planning. Trump is a far-rightist on issues such as immigration, but it is much like a Democrat in tax policy. In general, Trump's policy position is complex and cannot be accurately classified. 2 Hillary and Trump’s policy claims differ The economic policy agenda of Hillary and Trump's campaign for the US president essentially reflects the difference between the political and economic ideas of the Democratic Party and the Republican Party and the interests of the interest groups behind it. In short, the Democratic Party is a loyal follower of the Keynesian school. It believes in big governmentism and advocates expanding government power and advocating expansionary fiscal and financial policies. The Republican Party is more like a fan of the Chicago School, emphasizing individual freedom and autonomy, advocating "small government" and pursuing the traditional economic theory of laissez faire. Therefore, the ruling ideas of the two-party presidential candidates will be different. 2.1 Interest groups represented: Hillary represents labor and trade unions, Teplang represents employers and business owners, and Wall Street supports Hillary According to the political contribution data of the OpenSecrets website 1989-2014, it is possible to judge the interest groups represented by the two political parties. The political position of the Democratic Party is generally left-leaning. It has always been the representative of labor and guild. It is mainly concerned with concerns about labor rights, setting minimum wages, and increasing control over business. The supporting institutions mainly rely on law, media, media, universities, etc. The Lord, such as the University of California System and Harvard University, are the hardcore fans of the Democratic Party, and all donations go to the Democratic Party. The Republican Party is more representative of the interests of employers and business owners, supporting their companies to focus on energy and traditional manufacturing in the United States (automobiles, tobacco, pharmaceuticals, etc.). It is worth noting that everyone generally believes that the financial, financial services, defense, telecommunications and other industries are supporters of the Republican Party. In fact, these enterprises are generally wall-mounted, but only slightly favored by the Republican Party. For example, Bloomberg, the founder of Bloomberg News Group, was a Democrat. In 2001, he was elected as the mayor of New York as a Republican and later changed to a non-party. In the 2016 presidential election, the financial industry, overseas capital, and emerging high-tech industries represented by Wall Street and the capital choices behind them stood behind Hillary, indicating that the financial consortium’s choice of presidential candidates is not based on political stance. Or ideology, but depends on whether the candidate's policy is beneficial to him. Wall Street chose to support Hillary because it was even more reluctant to elect Republican presidential candidate Trump. According to the latest data from a US research institute, Wall Street's hedge funds and private bond companies raised $41.21 million in support of Hillary's group and its campaign, while Trump received only $230,000 from Wall Street. The logic behind Wall Street's choice of Hillary is very simple: they are willing to pay a little more tax, and they are not willing to risk losing their wealth and business. 2.2 Fiscal Policy Disagreement: Hillary advocates tax increase, Teplang advocates reduction of expenses From the election platform of the Democratic Party and the Republican Party, both candidates tend to stimulate the economy and reduce the unemployment rate. The financial means is nothing more than adjusting the tax rate and stimulating infrastructure, but whatever means is subject to the current debt ceiling. The U.S. finances have been in deficit for 16 consecutive years, and the debt ceiling has been mentioned to 18 trillion yuan, and will be further raised in March next year. Huge amounts of national debt and heavy interest burdens constrain the US government's fiscal stimulus. In this regard, the Democratic Party and the Republican Party have proposed different solutions. The Democratic Party wants to open source, while the Republican Party tends to cut costs. Hillary advocates a progressive tax system. The higher the income, the higher the tax rate, and the increase in financial resources by increasing taxes on the rich. This approach is similar to the way after Obama took office. After Obama took office, he canceled many tax relief policies for large companies in Bush’s term, which is also open source. Trump believes that the rich are the mainstay of investment and the main creator of wealth. Progressive tax rates can distort incentives and reduce production enthusiasm. He advocated reforming the US universal health care reform bill, arguing that the policy pushed up the government's medical expenditure costs, and abolishing the policy would help reduce government spending. In addition, Trump will also strategically contract in the diplomatic and military to reduce spending. However, it is foreseeable that the US fiscal deficit will continue in the short term. Although the two parties have different opinions on the solution to this problem, it is impossible for Hillary or Trump to really reduce government spending after taking office. Both economic policies have mentioned increasing infrastructure investment. According to the report of the American Society of Civil Engineers, the current infrastructure investment gap in the United States has reached 1.439 trillion US dollars, mainly distributed in roads and bridges, airports, ports, power grids, and water supply. Infrastructure in the field. Hillary plans to increase $275 billion in infrastructure investment in five years, while Trump hopes to switch to capital construction by shrinking diplomacy and foreign military spending. On the other hand, in the two campaign platforms, government spending remains high, but the focus is different. The Democratic Party is more inclined to spend money in education and medical care, while the Republican Party is more willing to raise defense spending. 2.3 Differences in monetary policy: Hillary may continue to loose , Teplang criticizes low interest rate policy Hillary and Trump do not currently present a clear monetary policy perspective, but we can analyze one or two from their remarks. Trump has repeatedly criticized the Fed's low interest rate policy, but his criticism of low interest rates is more about the negative impact of the policy, such as asset price bubbles and the false prosperity of the stock market. But this does not hinder his preference for low interest rates. He believes that low interest rates are good for long-term financing and can be used to repay high-interest old debts by issuing cheaper new debt. At the same time, it can reduce the financing cost of infrastructure investment. Trump’s seemingly contradictory approach is in fact consistent with the Republican “small government†philosophy that the government should not interfere with the Fed’s decision. If Trump comes to power, he will not interfere with the current Fed's monetary policy. In the framework of the Chicago School, he should be more inclined to let the market automatically correct the distortion caused by the low interest rate policy. Hillary did not have a clear conclusion on monetary policy. However, she tends to ease the deficit problem by raising taxes, so the monetary policy cannot be tightened too much, otherwise it is not conducive to the recovery of the US economy. Therefore, she should have a high probability of continuing the tone of monetary easing, and she may continue to intervene in the Fed’s rate hike to ensure that the US economic recovery is not interrupted. 2.4 Trade policy differences: Hillary is conservative but moderate, and Tepran is more radical and anti-global Hillary and Trump’s trade policies began to be conservative. In the context of the global economic downturn, trade protection and reverse globalization in the future will become the new normal. Although the "Trans-Pacific 601,099, buying Partnership Agreement (TPP)" during Secretary of State Hillary Clinton is single-handedly, now Hillary has turned against the TPP. Hillary’s October debate gave reasons for shifting her position. She believes that the current TPP is no longer in line with her standards and American interests. Her standard is to raise wages and create more jobs for the American people. In other words, her trade policy is to stop any trade agreement that hinders job growth and income growth. For companies whose headquarters are transferred overseas, Hillary recommends a “departure taxâ€. Trump's trade policy is more radical. To protect traditional industries, he has always advocated trade protectionism and opposed free trade agreements such as NAFTA and TPP. For China, he believes that China’s accession to the WTO has caused more than 50,000 factories in the United States to collapse and more than 10 million workers to be unemployed. He suggested that China be declared a currency manipulator and impose a 45% tariff on all Chinese imports. 2.5 Financial regulatory differences: Hillary advocates strengthening supervision, Trump advocates deregulation The market generally believes that Hillary Clinton as a Democratic candidate will continue Obama's regulatory policy. After the 2008 financial crisis, the Obama administration introduced the most comprehensive and severe financial reform bill, the Dodd-Frank Act, since the Great Depression, which strengthened the supervision of financial institutions. Hillary’s regulatory policy is mainly from her deputy Sanders, who strongly advocates rectifying Wall Street and dismantling big banks. Contrary to Saunders's financial policy, Trump believes that deregulation should be relaxed and that the Dodd-Frank Act should be abolished, which is in line with the Republican Party's consistent thinking. Although Trump's claim is more in line with Wall Street's interests, Wall Street is worried that his radical ruling will lead to greater uncertainty. The regulatory framework after the financial crisis has been determined. Wall Street may be more convinced that Hillary’s “regulatory strengthening†will not have much impact on their business. Instead, Trump’s election will lead to market turmoil and asset price decline. . 2.6 Disagreement between immigration policy and employment: Hillary supports immigration, Teplang wants to build walls to stop immigration Hillary and Trump’s immigration policies are very different. Hillary hopes to continue the Obama administration’s immigration policy, support illegal immigrant families who are chasing the American dream, and strive to get millions of illegal immigrant workers out of the shadows. Trump’s immigration policy is extreme. He claims to be building a wall on the Mexican border and expelling 11 million illegal immigrants. Trump's "wall-building" theory is in line with the interests of the bottom American people who have not shared the benefits of economic recovery and globalization. They are very resistant to illegal immigrants entering the United States, thinking that these people have taken their jobs, and Trump's voice caters to their mentality. However, reports from US employers show that there are nearly 6 million vacant jobs in the United States, while unemployed and underemployed people reach 10 million. That is to say, most of the unemployment is structural unemployment, and more immigrants can fill some of the job vacancies, bring more economic activities and promote growth. 2.7 Attitudes and Positions towards China: Hillary Clinton pulls back and pulls against China, Trump maintains a tough attitude In order to please the voters and speculate on China's issues, China, which has attacked the economy with a tough stance and its military strength, has often tried and tested in the US presidential candidate's campaign. During the white-hot stage of the US presidential election, the candidates of the two parties will inevitably take turns to stage the old tricks of attacking China and hit the "Chinese card" in their hands. In her primary campaign speech, Hillary Clinton once called China "the biggest abuser of global trade" and said that she "will promote the establishment of a fair arena for global trade once elected." She accused China of "using the disgraceful and unfair trade practices to tilt the arena to a side that is not conducive to American workers and businesses." In the nomination speech at the Philadelphia Democratic National Convention, Hillary mentioned China twice, all related to trade. In addition to trade issues, Hillary Clinton supports China's toughness on the South China Sea issue. As a proponent and staunch supporter of the "Asia-Pacific rebalancing" strategy, she believes that the strategy "is vital to US security." Hillary has expressed strong support for the Philippines’ submission of the dispute to the International Arbitration in The Hague. At the same time, Hillary believes that the United States cannot do without China's support and cooperation on issues such as the Korean Peninsula and climate change. She believes that North Korea is the primary security threat of the United States. "The United States and China may cooperate effectively on the DPRK issue." Trump’s policy stance on the Chinese issue is tough. Trump does not know much about China, but often criticizes China and blames the US's predicament on China's rise. In his first candidum speech, Trump mentioned China 23 times, twice the number of times he mentioned the United States. He accused China of making Americans unemployed. "Many Americans can't find a job because there is no job at all, and China takes our jobs." In addition, he also said that after the election, it will strengthen the US military deployment in the East China Sea and the South China Sea and deter China. Trump has limited understanding of China. From his self-exposed book list, the content is mostly negative. His many criticisms of China have mainly been to build momentum for the general election and to attack China as a means of election. The strong rise of China has caused panic among some people in the United States. Trump intends to incite people's feelings of disgusting Chinese and enhance their popularity. 2.8 Ideology, ethnicity, disagreement on other issues such as the world political structure Hillary’s external attitude is generally tough. The age of her birth and growth is the most prosperous era in the United States, and the United States has long been a world leader. Clinton, who grew up in this era, has unparalleled pride and pride in the country. She also believes that she has the obligation to maintain or even enhance the strength of the United States and its position in the world. Therefore, Hillary shows her own toughness and threats. Countries with world status in the United States are curbing. Hillary supports abortion, and she believes that she must simultaneously protect women's access to safe and legal abortions in law and practice. On racial issues, Hillary has been committed to promoting racial equality, which is reflected in her group of friends. Hillary supports gun control. She believes that 33,000 Americans die every year from guns. Now it is time to control the guns. Hillary supports clean energy, stressing that the next generation should not be exposed to the disasters caused by non-climate factors, and should be allowed to enjoy the benefits of using clean energy. Trump is tough on the outside world. He clearly defines extreme Islamic extremism, but he does not rely entirely on the military power of the United States. He expresses his desire to unite allies and conduct war on the battlefield, economically, informationly, and ideologically. Means to deal with Islamic extremists and make the United States safer. Trump’s policy position is conservative on domestic issues. He opposes abortion, but supports abortion in cases of rape or conceiving a mother's life; opposes same-sex marriage, considers same-sex marriage to be a state affairs rather than a federal matter; opposes the abolition of the death penalty, advocates a heavy criminal defamation; Strengthening historical education and comprehensively cultivating students' ability; emphasizing energy as the national lifeline; denying global warming and opposing greenhouse gas emission reduction measures; opposing gun control, insisting that "the right to hold guns is the premise of all other citizenship rights" and that "guns and crimes There is no direct relationship; condemning the politics of gold rights and opposing excessive government intervention in social life. 3 Possible development directions of China's trade policy 3.1 History of US Trade Policy with China The choice of US trade policy toward China is constrained by many factors. It is necessary to consider changes in the US foreign strategy and the transformation of the global political and economic structure, as well as the constraints of Sino-US political and economic relations. From an economic point of view, the choice of Sino-US trade policy should focus on protecting the development and employment of domestic industries in the United States; from a political perspective, the choice of trade policy should seek a balance point in curbing China's rise and cooperation in Sino-US international affairs. In the early days of the founding of New China in 1949, China and the United States were politically hostile. The United States imposed a "containment" trade policy on China, imposed economic blockades and trade embargoes on China, and promoted a triangular economic framework policy combining the United States, Japan, and Southeast Asia. To exclude China from the Asia-Pacific economic circle. Sino-US relations have been normalized in 1972, and the US trade policy toward China has also moved from blockade and containment to cooperation and openness. In July 1979, the Chinese and American governments signed the Sino-US Trade Relations Agreement, which gave each other MFN status. In 1980, the US Congress amended the Foreign Assistance Act of 1961 to allow US private companies to conduct business in China. In the second half of the 1980s, the international political situation was turbulent. The United States hopes that China will move closer to the capitalist world through economic exchanges and technology transfer. During this period, the US trade policy toward China was relatively loose. The United States has relaxed the level of trade control over China and signed cooperation agreements in various fields such as industrial technology, taxation, fisheries, nuclear energy, and telecommunications technology. However, after the disintegration of the Soviet Union and the drastic changes in Eastern Europe, under the model of American Cold War thinking, the United States assumed China as the main enemy of the future. Therefore, the development of Sino-US economic and trade relations has once again stagnated. In 1990, the US strategic focus shifted to the Middle East. The Bush administration lifted economic sanctions against China and Sino-US economic and trade relations have resumed normal development. During the Clinton administration, Sino-US political and economic relations have achieved rapid development. In 1998, Clinton's visit to China confirmed the "constructive strategic partnership" between the two countries and began negotiations on China's accession to the World Trade Organization. On November 15, 1999, China and the United States formally signed a bilateral agreement on China's accession to the WTO, laying the foundation for China's formal accession to the WTO. In 2000, the two houses of the US Congress passed the grant of PNTR treatment to China, marking the beginning of the US trade policy toward China gradually getting rid of the political relationship. After China's accession to the WTO, the trade volume between China and the United States has continued to expand. However, the expansion of the US trade deficit with China has led to an imbalance between Sino-US trade, which has led to the proliferation of new trade protectionism in the United States, and Sino-US trade frictions have continued to occur. Especially after the 2008 financial crisis, the United States repeatedly demanded the appreciation of the renminbi, further opened up the market for the purpose of protecting its own economy and curbing China’s economic development, and repeatedly implemented anti-dumping, countervailing, 337 investigations and various arrangements on Chinese goods. Trade protection measures such as non-tariff barriers have caused certain damage to the Chinese economy. On the other hand, with the rapid rise of China's economy, China's political and economic status in the world is becoming more and more important. In order to win China's support in international political affairs, the United States is paying more and more attention to cooperation and communication with China. The common interests of the country on issues such as anti-terrorism and nuclear security have made the political relations between the two countries relatively stable in recent years. 3.2 The future direction of Sino-US trade The history of Sino-US relations after the Cold War shows that tough and aggressive campaign speeches can easily lead to a tough policy of dialogue in the early days of the new presidential rule and create tensions between China and the United States. This has formed a cycle of recurring laws between China and the United States. In the election year of the United States, Sino-US relations will enter a "tight period", and Sino-US trade will also enter a period of "high friction." Clinton has an in-depth understanding of international affairs and will not support an extreme anti-globalization stance. She is generally open-minded in economic and trade relations. Otherwise, the "two-ocean strategy" will not be promoted at the beginning, that is, the Trans-Pacific Partnership Agreement. the current transition "(TPP) and" 600558, bUY agreement transatlantic trade and investment partnership "(TTIP) trade position is for the purpose of canvassing campaign, Hillary could not understand trade protection for the domestic economy and overall employment Impact. If Hillary comes to power, Sino-US relations and dialogue are expected to continue, and the economic, trade and political relations between the two countries cannot be changed drastically. This is also in line with the interests of the support behind them. Trump's trade proposition is isolationism. He believes that China's manipulation of the RMB exchange rate is the source of the decline of US manufacturing and employment. China’s large foreign exchange reserves and its huge trade surplus with the United States are also the result of China’s manipulation of the exchange rate, subsidies to enterprises and the destruction of free competition. Once Trump comes to power, the rise of US trade protectionism may have a new impact on Sino-US economic and trade relations, and Sino-US trade is likely to enter a "freezing period." 3.3 The Impact of Trade Protectionism on China's Employment in the United States Reducing the unemployment rate in the United States is an important reason for the US to implement a protectionist policy toward China. But when US interest groups lobby government officials to adopt protectionism on goods imported from China, the first consideration is not the employment and welfare of workers. This is because those interest groups that advocate trade protection against China are often industries that are subject to competition from Chinese products in Sino-US trade. China's exports of cheap goods to the United States will reduce its profits. However, once the protection measures are applied to these commodities, the import is reduced, and the price of American goods is increased. Thus, the amount of goods that can be purchased by the US consumer, the net value, and the information workers (including workers) is substantially reduced, and the social welfare level Below the state before trade protection. More importantly, the implementation of trade protectionism on the surface is conducive to reducing unemployment, and in fact it is the employment level of the entire private sector. After the 1990s, the trend of economic globalization has become increasingly apparent. As the leader of developed countries, the United States has also joined the general trend of global industrial transfer. Labor-intensive manufacturing industries represented by textiles and garments and capital-intensive manufacturing industries dominated by steel and petrochemicals began to move to emerging markets. The industrial structure of each country has undergone significant changes. The position of American manufacturing in the overall economic structure is declining. The change in industrial structure first led to changes in the employment structure, and the proportion of employment in the manufacturing sector declined. In other words, China's exports are not an internal factor that leads to the decline of domestic industrial and unemployment in the United States. The shift in the US manufacturing industry brought about by changes in industrial structure is the root cause. Changes in the industrial structure have also caused an escalation of the trade structure. With the development and expansion of the tertiary industry in the United States, especially the service industry, the proportion of its trade in services exports has gradually increased, while the trade in traditional manufacturing has shrunk. As of September 2016, the employment of the US service industry accounted for as much as 84%. Exhibit 1: US manufacturing output as a share of GDP continues to decline Source: Wind, Founder Securities 601901, Buy Exhibit 2: US manufacturing employment accounted for a decline Source: Wind, Founder Securities 4 If Hillary or Trump is elected president of the United States: Governing ideas and influence on the market Hillary’s policy ideas are more about the continuation and revision of the current Obama administration’s thinking. Trump, on the other hand, represents a policy of “changing the stringsâ€. Because his policy ideas are more radical, he has raised concerns about the uncertainty of the market, but it also reflects the demands of the people for change. In general, Hillary and Trump's campaign platforms mostly implement the political policy of their representatives. 4.1 If Hillary is elected president of the United States Hillary’s policy ideas are more about the continuation and revision of the current Obama administration’s thinking. As a politician with rich experience, Hillary brings more certainty to the market. Hillary pursues the Keynesian school and big governmentism. On the one hand, it alleviates the deficit problem by raising taxes on the rich and cracking down on corporate tax exemption. On the other hand, while increasing investment in infrastructure investment, it increases education and The public service expenditure represented by the medical field is in line with the position of the employees and the middle class represented by the Democratic Party. If necessary, Hillary will use monetary policy to assist her fiscal stimulus, she should be more inclined to loose rather than tighten the currency. In the early days of the administration, Hillary Clinton may choose a conservative trade policy and continue to maintain Sino-US relations. In terms of financial supervision, the policy idea should still be within the framework of the Dodd-Frank Act. There should be no substantive strengthening of supervision in the short term. On the issue of immigration, Hillary hopes to continue the Obama administration’s immigration policy and support illegal immigrant families who are chasing the American dream. In her attitude toward China, Hillary supported the trade and the South China Sea issue, but at the same time cooperated with China on issues such as the Korean Peninsula and climate change. 4.2 If Trump is elected president of the United States Trump's policy is more radical, and there is no previous ruling experience, which brings greater uncertainty to the market. Trump pursues liberalism and the policy is right. Trump will ease the deficit problem by reducing government spending, and on the other hand, by reducing taxes and stimulating infrastructure to stimulate the economy, it is in line with the position of employer and business owners of Republican representatives. Trump supports the abolition of the Obama administration's universal health insurance program and the cessation of new employee recruitment in government departments (except for defense and public health) to reduce government spending. Simplify the tax system and substantially reduce tax revenues to stimulate domestic investment and consumption, and guide private capital to participate in infrastructure construction through tax incentives to achieve balance of payments, rather than simply investing in infrastructure investment in the form of government investment. His reforms also include relaxation of regulation in the energy and financial industries. Trump expects that this economic plan will increase US GDP growth by 4% and generate 25 million new jobs. In terms of monetary policy, the work will focus on the distortion caused by the low interest rate policy, which is likely to accelerate the Fed’s rate hike. Trump’s immigration policy is extreme. He claims to be building a wall on the Mexican border and expelling 11 million illegal immigrants. Trump’s other policy focus is on trade protection policies and anti-globalization. In his speech on the 22nd, he announced that he would re-negotiate the NAFTA (North American Free Trade Agreement) or withdraw from the 2205 clause and announce his withdrawal from the TPP. Take a tough stance on China’s export trade and declare China a currency manipulator. 4.3 The impact of different candidates on the market Hillary’s coming to power indicates that the Fed’s monetary policy tightening will be lower than expected, and the stability of the early policies will also benefit the capital market and the US stock market. Uncertainty risks have fallen, and market risk aversion has gradually subsided, which is negative for gold prices. Hillary’s openness to foreign trade will drive the recovery of currency exchange rates in emerging market countries, especially those with a high degree of trade dependence in the United States, such as Mexico. With the pull of infrastructure investment and the slow recovery of the US economy, the overall US dollar index should be a slower trend. Trump's tax cuts are conducive to the recovery of private consumption and the recovery of private investment. Tax incentives in the infrastructure sector will also accelerate investment, and Trump's program will theoretically be more conducive to the rapid recovery of the US economy. Although the low interest rate environment can reduce the financing costs of infrastructure investment, Trump's remarks may indicate that the low interest rate policy may be adjusted in the future. The economy is accelerating recovery and the number of possible unexpected rate hikes is negative. The toughness of Trump’s foreign policy (including trade and diplomacy) has caused the market to worry about the stability of the future economy, and gold prices may rise in the early days of its administration. The isolationist trade policy also hits the foreign exchange markets and stock markets of emerging economies. Exhibit 3: The impact of three debates on the price of gold Source: Wind, Founder Securities Exhibit 4: Impact of three debates on emerging market currencies Source: Wind, Founder Securities Founder macro supply side reform series report: 81. “Seven major policy themes: mixed reform, PPP, debt-to-equity swap, rail transit, Shenzhen-Hong Kong Stock Connect, consumption, sponge cityâ€, October 19, 2016; 80. "PPP exceeds expectations: new opportunities or new shadow banks? ", September 21, 2016; 79. “Is China Falling into the Liquidity Trap: Causes and Responsesâ€, September 18, 2016; 78. "Who is this meeting, the causes and implications of the financial crisis triggered by the US interest rate hike", September 12, 2016; 77. "Restoring the Truth of China's Economy: Why Strong Production Demand is Weak, Macroscopically Microscopically Good", September 10, 2016; 76. “Debt-to-equity swap: short-term slow release risk, long-term depends on reformâ€, August 24, 2016; 75. “PPP: Stabilizing Growth and Activating Private Investmentâ€, August 21, 2016; 74. "The global economy has avoided the Great Depression, but it has fallen into a big stagnation: the theory, practice, effects and implications of negative interest rates," August 10, 2016; 73. “Restarting the Reform of State-Owned Enterprisesâ€, August 3, 2016; 72. "The decline of private investment is essentially a new round of national advancement and retreat", July 30, 2016; 71. “Supply-side reform breaks the ice, economy, policy and market outlook for the second half of the yearâ€, July 29, 2016; 70. “Moderately expanding aggregate demand and promoting supply-side reforms—interpreting the spirit of the 726 Politburo meeting, July 27, 2016; 69. "The Barbarians at the Door - American Leveraged M&A in the 1980s and Implications for China," July 19, 2016; 68. “Capital Market Performance during the Economic L-type†of Germany, Japan, Korea and Taiwan, May 17, 2016; 67. Why is private investment falling sharply? ", May 16, 2016; 66. From the Third World to the First World: The Story of Singapore, May 11, 2016; 65. “Slow release of credit risk, maintaining healthy development of bond marketâ€, May 5, 2016; 64. The Mystery of M1's Rise and Its Impact on the Economy, Inflation and Major Assets, May 4, 2016; 63. “The Challenges, Responses, Lessons and Implications Faced by Latin America in the 1980sâ€, May 3, 2016; 62. "Arousing the alarm of the Chinese economy? -- An objective analysis of Moody's S&P's downward revision of China's sovereign rating outlook, April 29, 2016; 61. The Mystery of the Rise and Fall of Commodities: Logic, Trends, Impacts and Risks, April 27, 2016; 60. “Calculation Reform: Reducing Taxes and Promoting the Development of Service Industryâ€, April 25, 2016; 59. “Causes, Degrees and Impacts of Inflationâ€, April 21, 2016; 58. “The Challenge, Response and Enlightenment of the Supply Side Reform of the British Thatcherâ€, April 19, 2016; 57. Challenges, Responses and Implications of Supply-side Reform in the Reagan Period of the United States, April 18, 2016; 56. Cost Reduction: Challenges, Responses, Risks and Opportunities, April 7, 2016; 54. Ten Questions about China's Economy (4-6): Ice and Fire, April 4, 2016; 53. Ten Questions about China's Economy (1-3): Ice and Fire, April 3, 2016; 52. “Looking at the future policy trend from the “two sessionsâ€â€, March 17, 2016; 51, "This time is different? - Current housing bubble and comparison of Japan and 2015 China stock market in 1991, March 16, 2016; 50. Challenges, Responses and Experiences of Japan's Supply Side Reform Period, March 14, 2016; 49. “Reform of State-Owned Enterprises: Pilot, Breaking and Opportunitiesâ€, March 7, 2016; 48. “The Birth, Crazy, Disillusionment and Lessons of the Japanese Real Estate Bubbleâ€, March 4, 2016; 47. "Foresight of the two sessions: steady growth of policies, reform of the supply side", March 2, 2016; 46. ​​Challenges, Responses, Risks and Opportunities for Real Estate Destocking, February 29, 2016; 45. “Service Industry Shortcomings: Problems, Causes, Responses and Opportunitiesâ€, February 26, 2016; 44. “Challenges, Responses, Risks and Opportunities for De-Capacityâ€, February 24, 2016; 43. "The Redemption of China's Stock Market: Cracking the Mystery of the Ras Putin Market," February 22, 2016; 42. “The Status Quo, Response, Risk and Investment Opportunities of De-Leverageâ€, February 19, 2016; 41. “Adjustment, Response and Experience in the German Supply Side Reform Periodâ€, February 16, 2016; 40. “Assessment of Risks and Impacts of Bill Violationsâ€, February 4, 2016; 39. Why do currency speculators dare to be enemies with central banks? - Currency Attack, Crisis Response and Reflection of Fixed Exchange Rate System, February 3, 2016; 38. “Risk Assessment of Stock Pledge and Bill Financingâ€, February 2, 2016; 37. "Three major judgments in 2016: economic L-type, reform is political economy and stock market recuperation," February 1, 2016; 36. “Supply-side reforms to break the ice – Prospects for the economy and capital markets in 2016â€, January 26, 2016; 35. Defending the Financial Land: Apocalypse of the Financial Warfare in Hong Kong in 1998, January 26, 2016; 34. “Economic L-type and supply-side reformâ€, January 24, 2016; 33. Will the Asian financial turmoil in 1997 be a comeback? ", January 22, 2016; 32. "Strengthening the bright future of China's economic reform and transformation - Studying the spirit of the important speech of General Secretary Xi Jinping, Central Party School", January 20, 2016; 31. Challenges, Responses and Implications of China's Supply-side Reforms from 1996 to 2000, January 17, 2016; 30. "A shares gradually return to normal, and the capital market undertakes an important mission in the supply-side reform", January 12, 2016; 29, "Five Central Prospects: Thirteenth Five-Year, Great Power Ambition", October 15, 2015; 28, "Sino-US Cross-Pacific Century Handshake - Review of the Results of the Visit to the United States on September 22-28", September 28, 2015; 27. “State-owned enterprise reform: “1†was introduced, “N†approachedâ€, August 18, 2015; 26. “Xintongzhou, New Beijing, New Olympicsâ€, August 17, 2015; 25. "Integration of Central Enterprises: Arrows on the Strings", August 10, 2015; 24. "New Beijing, New Capital, Xintongzhou", June 17, 2015; 23. "Integration of Central Enterprises: Elephants Dance", June 14, 2015; 22. "Internationalization of the Renminbi: Background, Routes and Impacts", June 1, 2015; 21, "How to change from fast cattle crazy cattle to slow cattle long cattle: Sino-US bull market comparison", May 19, 2015; 20. “Speeding up asset securitization, benefiting economic transformation and financial industryâ€, May 14, 2015; 19. “Top-level policy design towards the new normal: strong reform + wide currency + expansion of financeâ€, May 1, 2015; 18. Bull Market on Leverage: Status, Impact and Future, April 24, 2015; 17. “Central Bank Capital Injection Policy Bank: Oriented QEâ€, April 23, 2015; 16. “Registration System: Developing Direct Financing and Promoting Transformation and Innovationâ€, April 21, 2015; 15. "See the flower in the colorless place: see the future policy trend from the "two sessions"", March 16, 2015; 14. “Registration System: The Rise of Equity, the Foundation of Prosperityâ€, March 6, 2015; 13. "Foresight of the two sessions: steady growth of policies, Xiaoyangchun stock market", March 1, 2015; 12. "Reform and Going to Attack, Chinese Football is Uplifting", February 27, 2015; 11. “Listening to the thunder in silence: seeing the future trend from the 2014 statistical bulletinâ€, February 26, 2015; 10. “Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei: Building the Third Largest Growth Pole and Urban Agglomerationâ€, February 3, 2015; 9, "Niuer, you go slower: wait for reform and the real economy - comment on the supervision of the CSRC, the new regulations of the CBRC entrusted loans and the central bank's intentions of the goods," January 17, 2015; 8, "State-owned enterprise reform: top-level design is heavy, the big wind elephant dances", January 16, 2015; 7. “Financing and integration of pensions increases fairness and promotion of personnel mobilityâ€, January 15, 2015; 6. "The Bull Market on Leverage", January 8, 2015; 5. “The reform is entering a crucial year, and the fiscal force will increase the steady growthâ€, December 31, 2014; 4. "New Normal, 13th Five-Year and Reforming the Cow", December 12, 2014; 3. “Looking forward to the Central Economic Work Conference and the Second Wave of Reforming the Bullsâ€, December 11, 2014; 2. “Top 10 Conjectures and 3 Major Risks in 2015â€, December 4, 2014; 1. "Foresight of the Fourth Plenary Session: Providing Political Guarantee for Reform and Strengthening", August 24, 2014. pet sofa bed,sofa cover pet protector,pet sofa pad,pet sofa for large dogs AUTRENDS INTERNATIONAL LIMITED , https://www.petspetsdoggze.com